Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) allow users to trade digital assets directly from their wallets without relying on centralized platforms. Unlike traditional exchanges, DEXs rely on smart contracts to automate trading, giving users full control over their funds while maintaining transparency and security.
With dozens of DEXs available across multiple blockchains, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. In this article, we review the top 10 decentralized exchanges, compare their features, fees, and supported networks, and provide insights to help traders make informed decisions.
Top Decentralized Crypto Exchanges Compared
| Exchange | Supported Chains | Type | Trading Fees | Best For |
| Hyperliquid | Native Layer 1 only | Perpetual Futures DEX | Low fees and gas-free trading | Advanced derivatives and leveraged trading |
| Uniswap | Ethereum, Arbitrum, Base, Polygon | AMM spot trading | 0.05 –0.30% | Token swaps and liquidity provision |
| 0x Protocol | Ethereum, Optimism, Arbitrum, Avalanche | Aggregator/Infrastructure | Varies by integrating DEX | Aggregated liquidity |
| dYdX | Ethereum L2 (dYdX Layer 2) | Perpetual Futures DEX | 0–0.15% maker, 0.20% taker | Advanced derivatives and margin trading |
| SushiSwap | Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, Fantom | AMM spot trading | 0.25% per swap | Multi-chain token swaps and decentralized finance (DeFi) features |
| PancakeSwap | BNB Chain, Avalanche, Fantom, Polygon | AMM spot trading | 0.25% per swap | Low-cost swaps on multiple chains |
| Curve Finance | Ethereum, Polygon, Optimism, Avalanche | AMM Stablecoin DEX | 0.04%–0.50% depending on pool | Stablecoins |
| Raydium | Solana | AMM plus order book hybrid | 0.25% | Fast Solana swaps and DeFi features |
| Kuma (IDEX) | Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum | Hybrid DEX (Off-chain match, on-chain settlement) | 0.1%–0.35% | ERC-20 spot trading with advanced order types |
| ApeSwap | BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche | AMM spot trading | 0.25% | Multi-chain swaps, staking, and yield farming |
10 Best Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) in 2026 for Crypto Trading
1. Hyperliquid – Best decentralized exchange for perpetual futures trading
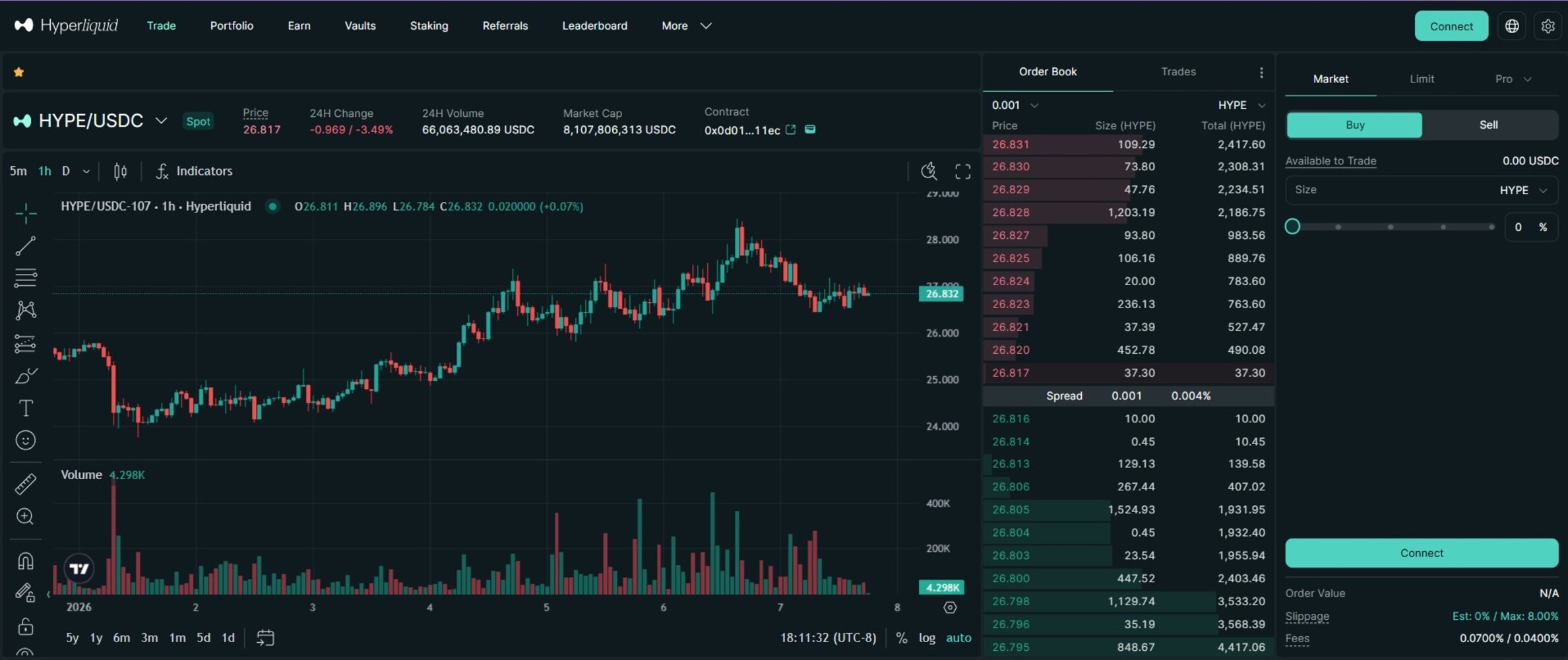

Hyperliquid is a decentralized exchange focused on perpetual futures trading. The protocol combines an on-chain order book with high-throughput infrastructure, enabling users to trade derivatives without relying on a centralized authority or custodial accounts.
The platform operates entirely on its native blockchain, which is optimized for low latency and fast transaction finality. This design enables real-time order matching and execution speeds comparable to centralized trading platforms while maintaining on-chain settlement and transparency.
Pros of Hyperliquid
- Fully on-chain order book with transparent trade execution
- Perpetual futures trading with leverage up to 50×
- No gas fees for order placement or cancellation
- Supports advanced order types and cross-margin trading
Cons of Hyperliquid
- Primarily focused on derivatives, with limited spot trading options
- High leverage increases risk for inexperienced traders
2. Uniswap – Best decentralized exchange for token swaps and liquidity provision
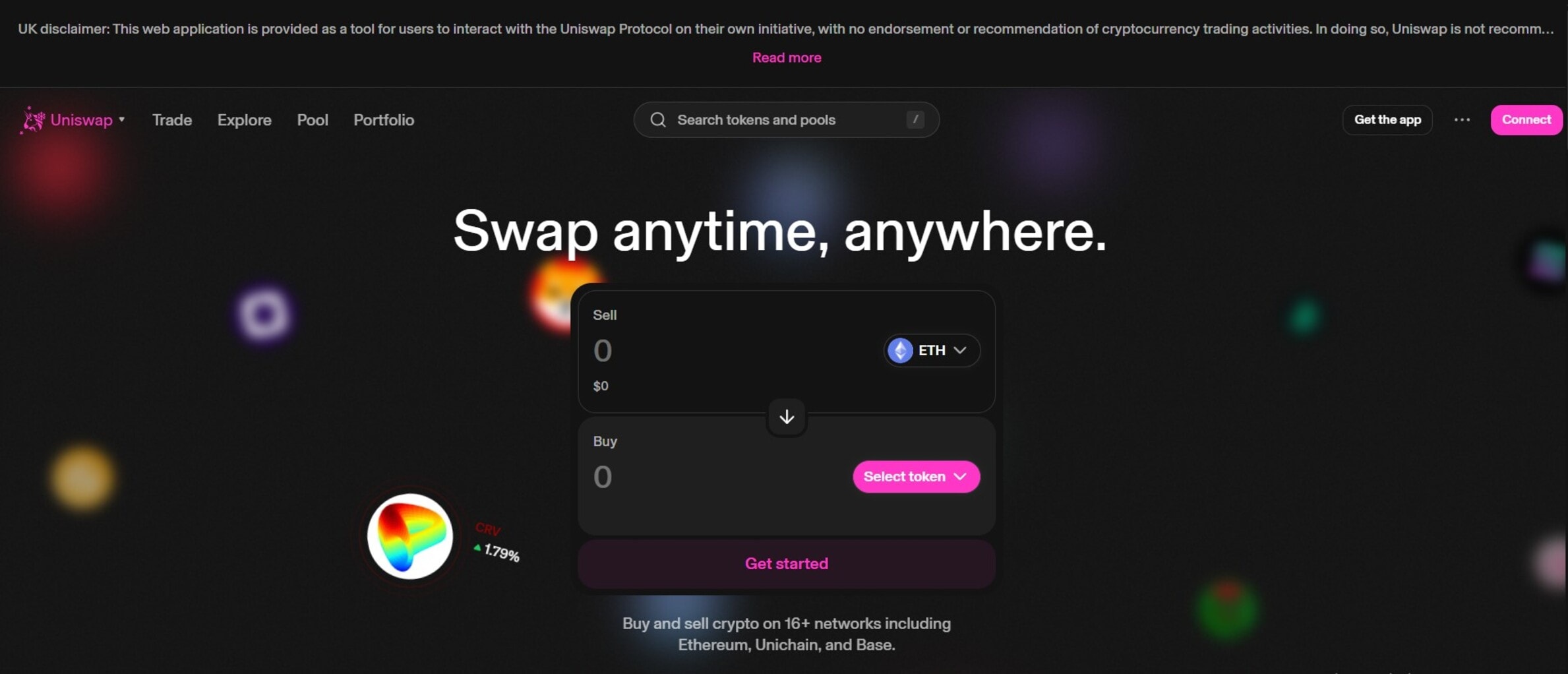

Uniswap is a decentralized cryptocurrency exchange designed for permissionless token swapping on Ethereum and other supported blockchains. It operates using an automated market maker (AMM) model rather than an order book, allowing users to trade directly against liquidity pools supplied by other users.
In addition to token swaps, the protocol allows users to provide liquidity to pools and earn a share of transaction fees. Uniswap has also introduced concentrated liquidity, which enables liquidity providers to allocate capital to specific price ranges to improve capital efficiency.
Pros of Uniswap
- Supports a large number of tokens and trading pairs
- Liquidity providers can earn fees from trading activity
- Fully non-custodial and open-source protocol
Cons of Uniswap
- Liquidity providers are exposed to impermanent loss
- Gas fees on the Ethereum mainnet can be high during congestion
3. 0x Protocol – Best decentralized exchange for aggregated liquidity

0x Protocol is an open-source decentralized exchange designed to facilitate token trading across multiple liquidity sources. Rather than operating as a traditional DEX with a single interface, 0x provides a set of smart contracts and APIs that developers and applications use to build trading experiences on top of its protocol.
0x Protocol’s modular design allows developers to integrate smart order routing, price discovery, and transaction execution without managing liquidity directly. This makes it a key piece of infrastructure within the decentralized finance ecosystem rather than a standalone consumer interface.
Pros of 0x Protocol
- Aggregates liquidity from multiple decentralized sources
- Widely integrated into wallets and DeFi applications
- Developer-friendly APIs and open-source architecture
Cons of 0x Protocol
- Not a consumer-facing exchange on its own
- Limited control over liquidity compared to native DEXs
4. dYdX – Best decentralized exchange for advanced derivatives trading

dYdX is a decentralized exchange focused on perpetual futures and margin trading. It is built for traders who need advanced tools without relying on centralized custody. The protocol allows users to trade crypto derivatives directly from their wallets, with all positions and settlements handled on-chain.
Pros of dYdX
- Order book-based perpetual futures trading
- Advanced trading tools suitable for experienced traders
- Cross-margin system for managing multiple positions
Cons of dYdX
- Primarily focused on derivatives rather than spot trading
- The interface may be complex for beginners
- Limited asset selection compared to spot-focused DEX crypto exchanges
5. SushiSwap – Best decentralized exchange for multi-chain DeFi access

SushiSwap is a decentralized exchange protocol that enables users to swap digital assets and provide liquidity across multiple blockchains. Originally built on Ethereum, the platform has expanded to support several Layer 1 and Layer 2 ecosystems, allowing users to access decentralized finance services beyond a single chain.
Pros of SushiSwap
- Supports multiple blockchains and Layer 2 networks
- Liquidity providers can earn fees and rewards
- Community-driven governance model
Cons of SushiSwap
- Gas fees may be high on some supported chains
- The feature set may feel fragmented compared to single-focus DEXs
6. PancakeSwap – Best decentralized exchange for low-cost trading on BNB Chain

PancakeSwap is a decentralized exchange built primarily on BNB Chain. It is designed to offer fast, low-cost token swaps using an automated market maker model. In addition to standard token swaps, PancakeSwap offers features such as liquidity provision, yield farming, and staking, which allow users to earn rewards by contributing assets to the protocol.
Pros of PancakeSwap
- Low transaction fees compared to Ethereum-based DEXs
- Fast trade execution on BNB Chain
- Wide range of supported tokens within the ecosystem
Cons of PancakeSwap
- Primarily centered around the BNB Chain ecosystem
- Additional features may introduce complexity for new users
7. Curve Finance – Best decentralized exchange for stablecoins

Curve Finance is designed to efficiently trade assets with similar value, such as stablecoins and tokenized versions of the same asset. The protocol uses a specialized automated market maker model that minimizes slippage and price impact, making it suitable for large trades involving stable-value tokens.
Pros of Curve Finance
- Extremely low slippage for stablecoin and similar-asset trades
- Supports multiple networks and Layer 2 solutions
- Supports governance through its native token (CRV), allowing users to participate in decision-making.
Cons of Curve Finance
- The interface may be less intuitive for new users
- Returns for liquidity providers depend on pool demand
8. Raydium – Best decentralized exchange for Solana-based trading

Raydium is a decentralized exchange built on the Solana blockchain that offers fast, low-cost token swaps. It integrates directly with Solana’s high-performance infrastructure to deliver near-instant transaction confirmations and minimal fees.
The protocol supports trading of SPL tokens and offers opportunities to provide liquidity, allowing users to earn a share of transaction fees by contributing to liquidity pools. Raydium also provides access to its order book via integration with the Serum decentralized exchange, combining AMM liquidity with on-chain order-book depth for more efficient trading.
Pros of Raydium
- High-speed transactions and low fees on Solana
- Combines AMM liquidity with order book depth via Serum integration
- Supports yield farming and staking opportunities
Cons of Raydium
- Limited to the Solana ecosystem and SPL tokens
- AMM mechanics can result in slippage for large trades
9. Kuma (formerly IDEX) – Best hybrid decentralized exchange
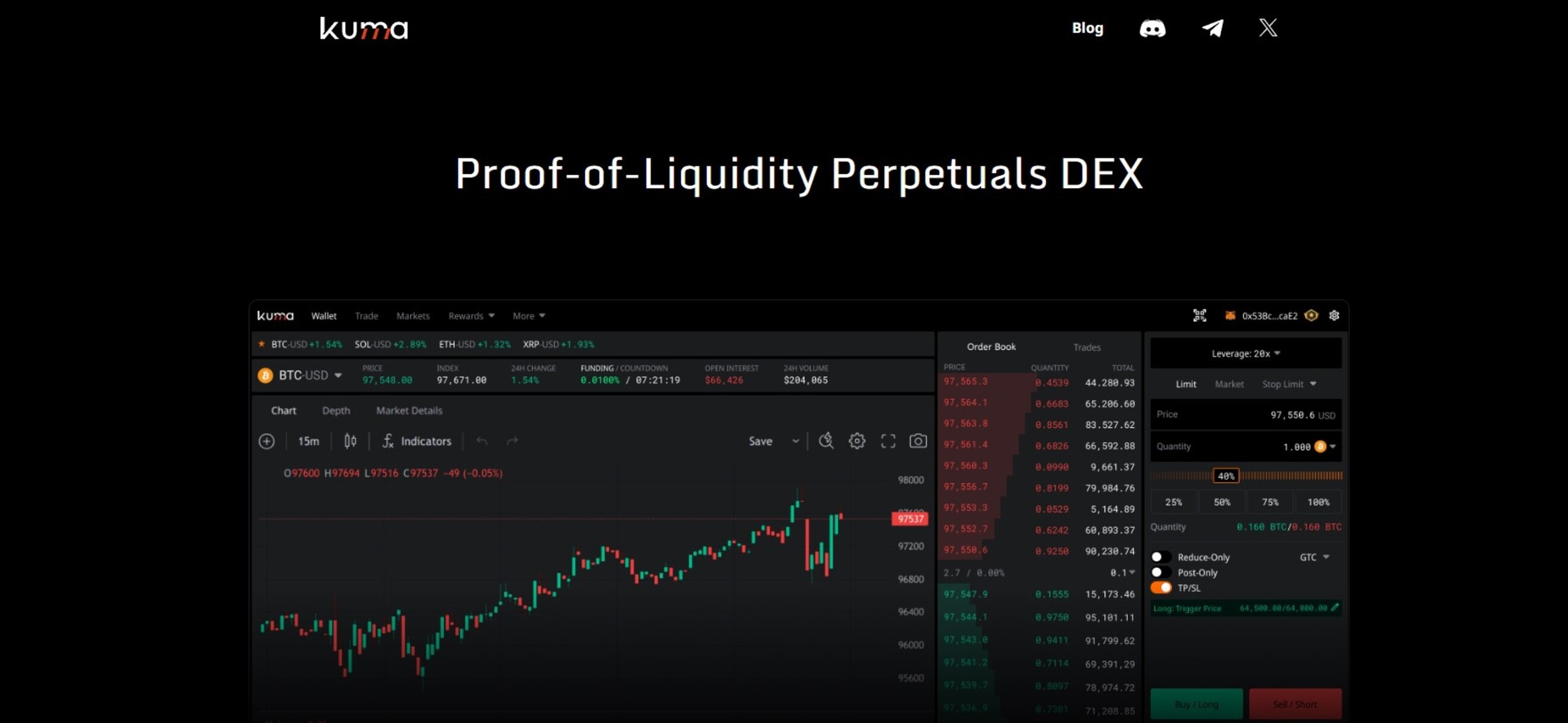

Kuma combines on-chain settlement with an off-chain matching engine to enable fast, efficient trading. This hybrid model allows users to trade ERC-20 tokens with low latency while maintaining self-custodial control of their funds.
The DEX supports limit, market, and advanced order types, offering features similar to traditional centralized exchanges. Kuma executes trades off-chain for speed and then settles them on-chain to ensure transparency and verifiability.
Pros of Kuma (formerly IDEX)
- Hybrid model combining off-chain matching with on-chain settlement
- Advanced order types, including limit and market orders
- Lower gas costs on supported Layer 2 networks
Cons of Kuma (formerly IDEX)
- Primarily limited to Ethereum and Layer 2 tokens
- Off-chain matching introduces dependency on Kuma infrastructure
10. ApeSwap – Best decentralized exchange for multi-chain DeFi

ApeSwap is built on the BNB Chain and offers token swaps, liquidity provision, and yield farming through an AMM model. The platform provides fast and low-cost transactions for BEP-20 tokens and has expanded to support other chains, enabling multi-chain DeFi access.
Pros of ApeSwap
- Low-cost token swaps on BNB Chain and other supported networks
- AMM-based liquidity pools with fee-earning opportunities
- Staking, yield farming, NFT, and launchpad features
Cons of ApeSwap
- Primarily focused on BNB Chain and BEP-20 tokens
- Liquidity depth varies across trading pairs and chains
What Is a Decentralized Crypto Exchange (DEX)?
A decentralized crypto exchange is a peer-to-peer marketplace that lets users trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets without relying on intermediaries. Unlike centralized exchanges (CEXs), which hold user funds and match orders on their servers, DEX crypto exchanges use smart contracts to automate swaps.
This non-custodial model gives users full control of their private keys, reducing the risk of hacks or platform failures. Benefits of DEXs include enhanced privacy, since many do not require Know Your Customer (KYC) or Anti-money Laundering (AML) verification.
They also provide censorship resistance and global access, aligning with crypto’s decentralized ethos. However, DEXs face challenges such as high gas fees on congested networks, lower liquidity for niche tokens, and front-running risks via MEV (Miner Extractable Value).
DEX vs CEX: Key Differences Explained
DEXs and CEXs are two primary ways to trade cryptocurrencies, but they operate differently. Here’s a side-by-side comparison:
| Feature | DEX | CEX |
| Custody | Users retain control of private keys | Exchange holds users’ funds |
| Order Execution | Automated via smart contracts | Matched off-chain by the platform |
| Liquidity | Depends on liquidity pools | Usually high, supported by the platform |
| Fees | Network/gas fees; trading fees may vary | Platform fees; no gas for users |
| Privacy | No KYC required | KYC verification required |
| Security Risks | Protocol risks, smart contract vulnerabilities | Platform hacks, custodial risk |
| Trading Features | Limited derivatives; mostly spot trading | Advanced tools, including margin, derivatives, and lending. |
| Accessibility | Global, permissionless | May restrict some countries |
| Examples | Curve Finance, Uniswap, and dYdX. | Binance, Bybit, and MEXC. |
Why invest in decentralized crypto exchanges?
Decentralized exchanges are more private and secure than CEXs, making them perfect for long-term holding. Since you hold and manage your private keys and your assets, there is no risk of losing your balance to platform hacks. The only thing to be wary of is keeping your keys safe because anyone who has this key can use them to access your account.
How to Use a Decentralized Exchange (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Connect Your Wallet
Open the DEX website and connect a compatible self-custodial crypto wallet, such as MetaMask, Trust Wallet, or Phantom. This allows you to trade directly from your wallet without giving up custody of your funds.
Step 2: Select Token Pair and Network
Choose the tokens you want to swap and the blockchain network you want to use. Make sure both tokens are supported on that network.
Step 3: Review Gas Fees and Slippage
Check the network fees (gas) for the transaction. Set your acceptable slippage tolerance to avoid unexpected price differences during execution, especially for volatile or low-liquidity tokens.
Step 4: Confirm and Execute the Swap
Double-check the details, then confirm the transaction in your wallet. Once approved, the smart contract executes the swap, and the tokens appear in your wallet after the transaction is finalized.
Benefits and Risks of Using Decentralized Exchanges
Benefits
- Non-Custodial Control: On a DEX crypto exchange, users hold their private keys, reducing the risk of hacks, theft, or insolvency that can occur on centralized trading platforms.
- Privacy and Anonymity: Most decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges do not require users to complete KYC or provide personal information. This protects user identity, making trading more private, and is particularly useful for individuals in regions with restrictive financial regulations.
- Global Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection and a compatible wallet can access a DEX. There are no geographical restrictions, and users from countries excluded by CEXs can still trade freely.
- Censorship Resistance: Transactions on a DEX are executed through smart contracts on the blockchain. This means no single entity can block trades, freeze accounts, or reverse transactions.
- Liquidity Provision Opportunities: Users can contribute tokens to liquidity pools and earn a portion of trading fees. This allows for passive income while supporting the exchange’s operations. Some DEXs also offer incentives, such as native token rewards for liquidity providers.
Risks
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Any bug, flaw, or exploit in the contract can potentially result in loss of funds.
- High Network Fees: Trading on blockchain networks like Ethereum can be expensive during congestion. Gas fees may sometimes exceed the value of small trades, reducing profitability for frequent or small-scale traders.
- Slippage and Price Impact: When trading low-liquidity tokens, the executed price can differ significantly from the expected price. Large trades can move the market, causing slippage and potentially higher costs.
- Limited Customer Support: There’s usually no centralized support team. If a trade fails due to network errors or if you send tokens incorrectly, there is little to no recourse.
Methodology: How We Chose the Best Decentralized Exchange
To identify the best decentralized exchanges, we reviewed 20 of the most popular decentralized exchanges across multiple blockchains. Our review focused on the factors that impact user experience, including privacy, security, liquidity, user experience, and more.
We considered liquidity because higher liquidity not only reduces slippage but also allows trades to execute faster and more efficiently. At the same time, we examined the range of supported tokens and networks, as platforms that operate across multiple chains provide users with greater flexibility and trading opportunities.
As stated earlier, security is another critical factor. We examined whether each protocol had undergone professional smart contract audits and maintained a consistent safety record. Alongside this, we evaluated additional features, including derivatives trading, staking, yield farming opportunities, and liquidity provision, since these options add value beyond basic token swaps.
Conclusion
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) offer a secure way to trade cryptocurrencies directly from your wallet. They combine privacy, self-custodial control, and global accessibility to deliver smooth and secure trading experiences for crypto investors.
While they may not always match CEXs in liquidity or advanced trading features, DEXs excel in transparency, censorship resistance, and providing opportunities to explore the decentralized finance world.
Choosing the best decentralized exchange depends on your trading goals, the crypto assets you want to trade, and your comfort level with blockchain networks and fees. But by understanding what each platform offers, you can navigate the decentralized ecosystem confidently and make informed decisions.
FAQs
The best DEX depends on your trading needs. For spot trading and token swaps, Uniswap or PancakeSwap are popular choices. For derivatives and perpetual futures, Hyperliquid or dYdX offer advanced tools and leverage. Consider factors like supported assets, fees, network, and user experience when deciding.
DEXs are generally safe because they give you more control of your funds. However, they rely on smart contracts, which can have vulnerabilities. Always check for audited protocols and avoid unverified tokens to reduce risk.
Gas fees are network transaction costs paid to blockchain validators. On networks like Ethereum, these fees can be high during congestion. Some DEXs on Layer 2 networks or alternative blockchains, like Binance Smart Chain or Solana, offer much lower fees.
DEXs built on low-cost blockchains usually have the lowest fees. PancakeSwap (BNB Chain) and Raydium (Solana) are known for fast trades with minimal transaction costs compared to Ethereum-based DEXs.




